In The Spotlight
The 21st International Conference and Exhibition on Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG2026) has opened at the Qatar National Convention Centre in Doha, underlining the pivotal role of LNG in supporting the global economy and Qatar’s leading position in the LNG industry
Delivering the conference’s opening address, His Excellency Saad Sherida Al-Kaabi, the Minister of State for Energy Affairs, the president and CEO of QatarEnergy, said, “It is a source of great pleasure to host this event at a time when QatarEnergy is emerging as a leading force in the energy sector in general, and in the LNG industry in particular, through its expanding role in meeting global energy markets needs and ensuring reliable supplies.
“The mega-projects we have launched a few years ago will more than double QatarEnergy's LNG production from 77 million tons per annum to 160 million tons per annum, including 142 million tons per annum from Qatar's North Field. Hereby, our projects will contribute about 40% of the new global LNG supplies over the next decade.”
H.E. Al-Kaabi provided an overview of the efforts to invest in expanding production, and storage, as well as emission reduction. Highlighting the LNG transportation sector, he said, “We have launched the largest shipbuilding programme in the industry's history, comprising 128 state-of-the-art LNG carriers with outstanding operational and environmental standards. We have already received 38 new vessels and will receive a new one every three weeks. This will give QatarEnergy the largest LNG carrier fleet in the world, reaching about 200 vessels within the next few years.”
Main achievements
His Excellency highlighted QatarEnergy’s main achievements as part of its strategic expansion programme in the petrochemicals sector, which will increase its polymer production capacity, both within Qatar and internationally, by about 235% compared to current levels, thus enhancing its ability to provide high-value products. This is in addition to increasing Qatar's production of condensates and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) by about 60% and helium by 115%.
He added, “QatarEnergy is working to support global food security by establishing a new world-class urea fertilizer production complex, which will increase its current production capacity by more than 110%, becoming the world's largest urea exporter. With this, QatarEnergy will become, within the next few years, the world's largest exporter of LNG, chemical fertilizers, and helium."
At a plenary panel discussion with the CEOs of QatarEnergy’s partner international energy companies H.E. Al-Kaabi forecast increasing demand for gas, driven by global economic growth and other factors like artificial intelligence and data centres, while oil “will be needed for a very long time”.
The session titled “Global LNG Dynamics: An Industry Perspective” was held with the participation of Patrick Pouyanné, chairman and CEO of TotalEnergies, Darren Woods, executive chair and CEO of ExxonMobil, Wael Sawan, CEO of Shell, and Ryan Lance, CEO of ConocoPhillips.
H.E. Al-Kaabi said, “QatarEnergy, along with its partners represented on the panel, are building LNG for the future with the lowest carbon footprint you can have. Everywhere where you'll see exploration blocks that are looking for oil or gas, you'll find QatarEnergy working there.”
His Excellency stressed that the world cannot live without energy. “People need to be prosperous, including about a billion people don't have the basic electricity that we enjoy. We can't deprive them of that growth.”
H.E. Al-Kaabi highlighted the importance of demand in driving the LNG industry, and while pointing out to Asian economies that are driving the main demand, His Excellency said “we must not forget the Middle East region, where gas is required in many parts as population growth requires additional power for continued growth that often comes from gas complemented by renewables.”
He stressed, “We are doing our best to develop and adopt the best technologies to reduce emissions, including CO2 sequestration in order to deliver the most affordable energy to the market in the most environmentally responsible manner. It is important for policymakers to be realistic about what can and cannot be delivered. They need to listen to the people who understand the business.”
QatarEnergy is organising LNG2026 in cooperation with the International Gas Union, the Gas Technology Institute, and the International Institute of Refrigeration, and with the participation of prominent speakers and leading figures in the global LNG industry. The four-day LNG2026 conference programme includes panel discussions with industry leaders and experts, and interactive debates on key topics, including the competitive advantages of LNG and its role in meeting global energy demand.
The conference is expected to draw about 4,000 participants and 16,000 visitors, while the accompanying exhibition features over 300 exhibiting companies. QatarEnergy is participating with an 800-square-meter pavilion showcasing its history and its role as one of the world's largest LNG producers.
On the sidelines of the event, QatarEnergy signed a 27-year Sales and Purchase Agreement (SPA) with JERA, Japan’s largest power generation company, for the supply of up to three million tons per annum (MTPA) of LNG from Qatar to Japan, with deliveries starting in 2028. QatarEnergy also signed a MoU with Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade & Industry (METI) and JERA to supply Japan with additional LNG during emergency situations.
Across the Middle East, oil and gas operators are acquiring larger, denser and more complex seismic datasets to unlock increasingly subtle geological targets
But as data volumes grow into the hundreds of billions of traces, the real challenge is no longer just acquisition. It is how quickly and confidently those datasets can be turned into actionable insight.
When growing data volumes are coupled with modern processing and imaging algorithms, such as elastic multi-parameter full waveform inversion, and the continued rise of artificial intelligence (AI) based workflows, the result is that high performance computing (HPC) systems are being pushed harder than ever. This of course intensifies demands on power, cooling and scalability. For energy giants, a key challenge is ensuring their HPC infrastructure remains fit-for-purpose to keep pace with modern geoscience.
Global technology company DUG is known for its state-of-the-art software and its network of some of the largest supercomputers on Earth. Against a constantly evolving hardware landscape, the Australian-born company is keeping its edge with the deployment of 82 new NVIDIA H200 machines, adding 41 petaflops of compute power to its global data-centre capacity. Each machine delivers an order-of-magnitude performance uplift over DUG’s fastest CPU-only hardware, further reducing the company’s turnaround times across both testing and production workflows.
The operational realities of a modern HPC facility also present significant opportunities for reducing both cost and environmental footprint. One way that DUG has maximised the energy efficiency of its HPC ecosystem is through the use of immersion cooling – where servers are submerged directly into a fluid that removes heat far more effectively than air. The technology supports significantly higher compute density, reduces power consumption and creates a stable environment without hot spots, dust or oxidation. Immersion allows operation at higher temperatures compared to air-cooling, thereby also reducing reliance on evaporative cooling, allowing hybrid or dry-cooling configurations that lower water use. This ultimately makes efficiency and sustainability part of the same design.
“Our data-centre upgrade significantly increases our total compute power,” said Harry McHugh, chief information officer at DUG. “This translates to even faster delivery of huge datasets and more computationally intensive workloads, from AI-inference applications, to advanced seismic processing and imaging workflows, including our revolutionary DUG Elastic MP-FWI Imaging technology”,
“Designing and operating at this scale gives us intimate knowledge of what modern HPC demands in practice – and this expertise drives the solutions we build and operate for our clients.”
With its new Abu Dhabi office supporting large-scale projects across the region, and a technology stack built around energy-efficient HPC and advanced imaging algorithms, DUG is primed to power the next wave of discovery in the Middle East, delivering faster, clearer and more reliable subsurface insights.

KOGS 2026 will serve as a strategic platform for high-level dialogue, technical excellence, and cross-industry collaboration. (Image source: SPE)
The Kuwait Oil & Gas Show and Conference (KOGS 2026), taking place from 3–5 February 2026 at the Grand Hyatt Kuwait and The Arena, is set to reinforce Kuwait’s position as a regional and global energy leader
Hosted by Kuwait Petroleum Corporation (KPC) and organised by the Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE), KOGS 2026 will bring together senior government officials, global energy leaders, technical experts, and innovators to address the opportunities and challenges shaping the future of the energy industry.
Held under the theme “Shaping Tomorrow’s Energy,” KOGS 2026 will serve as a strategic platform for high-level dialogue, technical excellence, and cross-industry collaboration.
The conference programme will feature high-level ministerial sessions, CEO plenary discussions, strategic panels, and a comprehensive technical programme, presenting peer-reviewed papers and expert-led sessions. Core focus areas include digital transformation and artificial intelligence, asset optimisation, decarbonisation, carbon management, energy efficiency, and emerging technologies supporting resilient upstream and integrated energy operations.
KOGS 2026 will also feature dedicated programmes including the Emerging Professionals Forum (EPF), alongside initiatives designed to support knowledge transfer and talent development.
The KOGS 2026 Awards will recognise outstanding achievements and forward-thinking contributions across the energy sector. They will celebrate excellence in academic achievement, sustainability and energy transition, AI digital transformation, excellence in regional project delivery, diversity, equity & inclusion in workplace culture, while spotlighting individuals and organisations shaping the future of energy through young professionals.
Complementing the conference, the KOGS 2026 exhibition will bring together leading regional and international companies to showcase advanced technologies, oil derivatives, and services that support operational performance, safety, and sustainability across the energy value chain, providing a dynamic platform for networking, collaboration, and business development.
KOGS 2026 sponsors include KPC, Alkhorayef Fawares Petroleum, Kuwait Drilling Company, NESR, Shell, SLB, Zain, Baker Hughes, Action Energy, Halliburton, Saudi Arabian Chevron, , bp, KJO, Total, Senergy Holding, Rock Flow Dynamics, International Marine Construction Co, Tomax, Abraj Energy, Abraaj Energy, Superior Energy, NOV, MEOFS, ROSENXT and STRATEGY&.
Ahmed Al-Eidan, chief executive Officer of Kuwait Oil Company, said, “This year’s programme reflects the depth and ambition of KOGS 2026. High-level ministerial and CEO plenary sessions will offer strategic insights into geopolitical dynamics, energy economics, and responsible resource development, alongside a comprehensive technical conference and exhibition showcasing innovation, knowledge exchange, and industry best practices. Together, these elements reinforce Kuwait’s pivotal role in shaping the future of energy.”
For more information and updates, see the website here:
-

Exclusive Interview with Friedrich Portner, Maritime Cluster, AD Ports Group
-

Exclusive Interview with Kevin Killeen, MSA Safety
-
Exclusive Interview with Maurits van Tol, Johnson Matthey
-

GPT Industries - Iso-Smart
-

ADIPEC 2024 - Exclusive Interview with Joseph El Bitar, Hexagon
-

ADIPEC 2024 - Exclusive Interview with Alexander van Veldhoven, Bapco Energies
-
ADIPEC 2024 - Exclusive Interview with Friedrich Portner, Safeen Group
-

ADIPEC 2024 - Exclusive Interview with Kevin Brilz, Fishbones
-
ADIPEC 2024 - Exclusive Interview with Mohamed Malak, Fishbones
-

ADIPEC 2024 - Exclusive Interview with Dileep Divakaran, SLB
-

ADIPEC 2024 - Exclusive Interview with Eric Kjol, SLB
-
ADIPEC 2024 - Exclusive Interview with Dmitry Shubenok & Aleksandr Dolgikh, North Side
-

ADIPEC 2024 - Exclusive Interview with Adam Stephenson, AkzoNobel
-

ADIPEC 2024 - Exclusive Interview with Frazer Young, Oil States
-

ADIPEC 2024 - Exclusive Interview with Peter Foith, CS Combustion Solutions GmbH
-
Exclusive interview with Maurits van Tol
-

Rockwell Automation interview with Sebastien Grau

The strategic partnership agreement sets out the framework for NOC and MOL to exchange information and jointly explore potential areas of cooperation. (Image source: Adobe Stock)
Hungary’s MOL Group has signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with Libya’s National Oil Corporation (NOC) for cooperation in hydrocarbons exploration, technological innovation and crude trading, as international interest in Libya hots up
The strategic partnership agreement sets out the framework for NOC and MOL to exchange information and jointly explore potential areas of cooperation. These include hydrocarbon exploration and production, technological and field development innovations, oilfield services opportunities in Libya, crude supply and trading activities.
"We recognise Libya’s oil and gas industry as a pillar of strength and expertise. I am sure that this new agreement will act as a catalyst for further expanding our international portfolio, creating clear mutual value for both companies and reinforcing the resilience of our region. From the perspective of security of supply and energy sovereignty, particularly for landlocked countries, diversification of sources is of crucial importance. Our cooperation also goes beyond business, as we have agreed to rebuild our educational, scientific, and university ties in order to learn as much as possible from each other. Such partnerships can also help Europe to find its own path to competitiveness, rather than switching between different forms of energy dependency,” – said Zsolt Hernádi, chairman and CEO of the MOL Group.
The agreement comes as MOL is looking to expand its international portfolio to maintain its strategy target of at least 90,000 barrels of oil equivalent/day production level over the next five years, recently signing cooperation agreements with the national oil company of Kazakhstan (KazMunayGas), the national oil company of Azerbaijan (SOCAR), and the national oil company of Türkiye (Turkish Petroleum). The company has oil and gas exploration and production assets in nine countries, with production in eight countries: in Croatia, Azerbaijan, Iraq, Kazakhstan, Russia, Pakistan, Egypt, and Hungary.
The agreement also reflects the hotting up of international interest in Libya. Chevron recently signed an MoU with NOC to evaluate exploration and development opportunities, while TotalEnergies has signed an agreement extending the Libya Waha Concessions up to 2050, paving the way for further investments. TGS has a global provider of energy data and intelligence, has just signed a Letter of Intent (LOI) with North Africa Geophysical Company, (NAGECO),a subsidiary of the NOC to advance high-quality subsurface data, supporting Libya’s upstream development through modern, fit-for-purpose data and technology solutions. Libya’s latest upstream licensing round launched in March 2025, the first in 18 years, has attracted more than 40 bids, signalling growing international interest in Libya’s largely untapped hydrocarbon potential.
Global energy consultancy company Penspen scooped US$500mn in new contract awards in 2025, up 120% on 2024, underpinned by growth in its core Middle East market
The achievement reflects a year of strong global performance across engineering, project management consultancy (PMC) and asset integrity services, the company says.
In the Middle East and Africa, Penspen was awarded 65 new contracts worth US$456mn, spanning project management supervision and consultancy services, FEED, detailed design and integrity assessment. The UAE remained its largest and most strategic country of operation, supported by deep engagements across the ADNOC Group, where Penspen is one of the ADNOC Groups top-20 energy sector contractors operating in the UAE.
During the year, Penspen secured and executed a number of high-value PMC assignments supporting critical gas infrastructure, including LNG pre-conditioning, compression facilities, utilities and production enhancement programmes, alongside multiple offshore and onshore PMC packages.
In Saudi Arabia, Penspen concluded 12 new agreements spanning studies, FEED, detailed design and project management supervision services. It continued to build momentum through its selection under a framework with ENOWA, executed through a joint venture with Dar Al Handasah and in collaboration with Technip, positioning Penspen at the heart of NEOM’s next-generation energy and water infrastructure.
Neale Carter, executive vice president, Middle East, Africa and Asia Pacific Regions, said, “ The Middle East played a pivotal role in Penspen’s 2025 growth, contributing the largest share of new contract awards and reinforcing the region’s role as a strategic engine for the business.
“Our long-standing relationships across the UAE and Saudi Arabia, combined with our ability to deliver complex gas, LNG infrastructure and PMC programmes at scale, continue to differentiate Penspen in a highly competitive market. With sustained investment across gas, energy security, aviation, and transition-linked infrastructure, we see significant opportunity to build on this momentum in the years ahead.”
In addition to the Middle East and Africa, Penspen also saw strong growth in Europe and the Americas, supported by major infrastructure and energy transition programmes.
In the UK and Europe the company won 177 new contracts worth US$16mn, including fuelling terminal operations, pipeline maintenance and inspection, hydrogen repurposing and blending, carbon capture studies, gas compression upgrades and pipeline diversions
While in the Americas it secured 54 new contracts worth US$5mn, including pipeline fitness-for-service, electrical interference and cathodic protection studies, gas pipeline project management, production operations support and environmental testing.
Chief executive officer, Peter O’Sullivan, said, “With cumulative contract awards of US$500mn, 2025 stands out as one of the strongest commercial and delivery years in Penspen’s history.
“While we continued to build momentum across Europe and the Americas – particularly in energy transition – our performance was anchored by exceptional delivery in core markets where demand for large-scale, complex energy infrastructure remains strong.”
Aramco, Honeywell and King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) are collaborating to scale up the development of Crude-to-Chemicals (CTC) technology in a bid to maximise the value of crude oil and reduce costs associated with CTC conversion
The new CTC pathway will entail converting crude oil directly into light olefins and other high-demand chemicals, resulting in improved fuel efficiency, carbon utilisation, and process economics—allowing for more efficient and cost-effective production at scale.
The collaboration aligns with Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 by helping to advance economic diversification, build national research and technology capabilities, and strengthen the Kingdom’s position in the global chemicals market, combining academia and industry expertise to accelerate technology development and national capabilities.
Dr. Ali A. Al-Meshari, Aramco senior vice president of technology oversight & coordination, said, “This collaboration with Honeywell UOP and KAUST furthers Aramco's efforts to drive innovation and shape the future of petrochemicals. By harnessing the power of cutting-edge technologies, we aim to enhance energy efficiency and unlock increased value from every barrel of crude. This novel Crude-to-Chemicals process is aligned with our vision of supporting the global transition towards cleaner, high-performance chemical production. Moreover, this initiative demonstrates our focus on contributing to the growth of a vibrant ecosystem, where the deployment of innovative technologies can create lasting value for our stakeholders, our communities, and the environment.”
Rajesh Gattupalli, Honeywell UOP president, added, “This agreement marks a defining moment in our strategic collaboration with Aramco and KAUST – and in the global evolution of Crude-to-Chemicals technology. With Honeywell UOP’s deep expertise in catalytic process design and commercial scale-up, we’re well positioned to drive this innovation forward.”
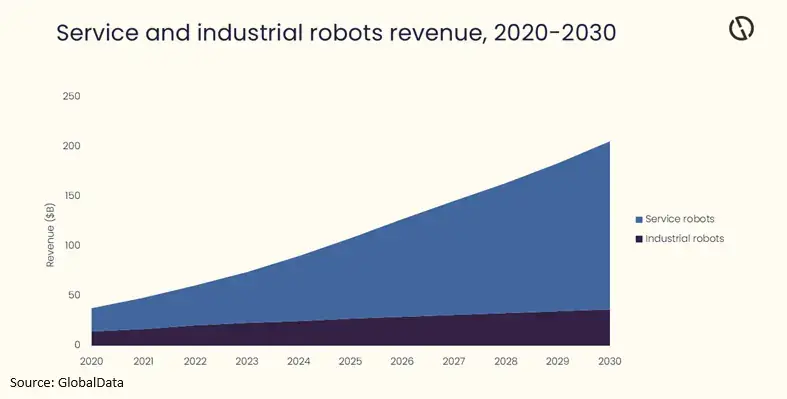
The global oil and gas robotics market is forecast to hit US$205.5bn in 2030. (Image source: GlobalData)
The global oil and gas robotics market is forecast to grow from US$90.2bn in 2024 to US$205.5bn in 2030, according to data analytics and consulting company GlobalData
Robotics is rapidly transforming oil and gas operations as advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud computing unlock the next phase of industrial automation. Previously focused on repetitive industrial tasks, robots can now operate autonomously, collaborate, and access cloud-based data in real time. AI enables advanced decision-making, navigation in complex environments, and reduced reliance on human intervention.
Despite progress in humanoid robotics, task-specific robots remain dominant. GlobalData’s Strategic Intelligence report, “Robotics in Oil and Gas,” highlights how robotics is increasingly being adopted across the oil and gas value chain to improve safety, efficiency, and asset integrity.
Operators such as Equinor deploy subsea autonomous vehicles, including Hydrone-R, for extended underwater inspections, while Shell uses Cyberhawk drones and Sensabot robots for aerial and ground-based inspection of flare stacks, tanks, and pipelines. BP and Chevron have trialled Spot quadruped robots to autonomously survey facilities and collect visual, thermal, and methane data, reducing personnel exposure to hazardous environments. While ADNOC deploys more than 65 robotics applications across its operations.
Ravindra Puranik, Oil and Gas Analyst at GlobalData, comments: “Autonomous robotic systems are being introduced across hazardous, remote, and offshore environments to perform inspection, surveillance, and monitoring tasks without continuous human control.”
These platforms deliver higher operational efficiency through faster inspection cycles, consistent task execution, and repeatable, high-quality data capture, independent of operator skill or availability.
GlobalData notes that offshore and subsea operations remain a major focus area for robotics deployment. Remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) continue to support real-time subsea inspection, maintenance, and intervention, while autonomous underwater vehicles enable long-duration seabed surveys and pipeline monitoring with reduced reliance on surface vessels.
Puranik concludes: “While challenges remain, the integration of robotics with digital twins, edge intelligence, and predictive analytics is accelerating. As these technologies mature, robotics will move beyond supporting roles to become indispensable operational assets, across the oil and gas industry.”
Despite advances in digital technology, many oil and gas sites across the Middle East still rely on manual entry for tank and vessel inspections, resulting in days of downtime, high scaffolding costs and risk to human life
What if you could change all that with drone technology?
Inspections drones such as the Elios 3 are revolutionising the world of confined space inspections, improving safety, reducing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency.
Join us for an exclusive live webinar hosted by Flyability in association with Oil Review Middle East on ‘Transforming oil and gas operations with the Elios 3 drone’ on Tuesday 2 September at 2pm GST. Industrial experts will explain how drones such as the Elios 3 are transforming confined space inspections, and how you can integrate this technology into your operations seamlessly.
Key highlights:
Drone integration: learn how to safety and effectively implement drones in confined space
Safety and training: understand essential safety protocols and training strategies for your team
ROI: discover how to measure and achieve a strong return on investment with drone technology
Real world use cases: hear from the engineers using drone tech in the field on the impact Elios 3 is having on in oil and gas inspections.
Speakers and host:
Fabio Fata – senior sales manager, Flyability (moderator)
Eralp Koltuk – inspection lead engineer, Tüpraş
Danijel Jovanovic – director of operations, ZainTECH
Take your operations to the next level! Don’t miss out on gaining valuable insights into how drones can make inspections safer, faster and smarter .
From making inspections in hazardous confined spaces much safer to streamlining the whole process and providing valuable real-time data, you will get to see exactly how the Elios 3 is changing the game.

Progress has been reported in developing action plans to reduce methane emissions and end routine flaring. (Image source: Adobe Stock)
Coinciding with COP30, significant progress has been reported in driving forward the aims of the Oil & Gas Decarbonization Charter (OGDC) launched at COP28
The Oil & Gas Decarbonization Charter (OGDC), a global coalition of leading energy companies championed by the CEOs of ADNOC, Aramco, and TotalEnergies and supported by the Oil and Gas Climate Initiative (OGCI), highlights expanded reporting coverage, strengthened action plans for emissions reduction and enhanced collaboration to accelerate industry decarbonisation in its 2025 Status Report: Implementing Action.
The Charter now brings together 55 signatories operating across more than 100 countries, representing around 40% of global oil production. Signatories invested approximately US$32bn in low-carbon solutions including renewables, carbon capture, hydrogen and low-carbon fuels in 2024.
This year, for the first time, the companies shared emissions data based on the OGCI Reporting Framework, laying the foundation for consistent reporting across 55 companies. 50 of the 55 signatories submitted data for this year’s report, covering 98% of OGDC operated production, most of which has received third-party assurance.
Forty-two signatories have now set interim Scope 1 and 2 emissions reductions ambitions for 2030, and 36 have developed corresponding action plans, reflecting tangible progress since the Charter’s 2024 Baseline Report, with six more companies sharing interim ambitions and seven more developing corresponding action plans on methane and flaring.
Extensive collaboration programme
An extensive collaboration programme is underway, with a focus on methane, flaring and reporting. TotalEnergies for example is sharing its AUSEA technology with several national oil companies to strengthen methane detection and measurement. Peer-to-peer exchanges, regional partnerships and technical workshops have strengthened capacities, while engagement with OGCI, the United Nations Environment Programme, the World Bank and many others, are helping scale practical solutions. At the company level, OGDC is helping to embed tailored, industry-specific training programmes.
Dr Sultan Ahmed Al Jaber, managing director, Group CEO of ADNOC, COP28 president and OGDC CEO Champion, said, “Two years ago, at COP28 we came together to create the world’s first truly industry-wide coalition to decarbonise at scale. Together, we are turning the Charter’s words into action by delivering tangible progress, scaling innovation and reporting transparently against our shared commitments.”
Patrick Pouyanné, chairman and CEO of TotalEnergies and OGDC CEO Champion, added, “OGDC is about action and collective delivery. This year we moved from baseline to implementation, with almost all signatories reporting data that covers 98% of operated production and more companies setting 2030 targets backed by plans. This reflects that progress starts with what we measure and a shared reality that this is a journey where we advance faster together. Our focus now is clear. We must cut methane, end routine flaring and report progress consistently. We invite all IOCs and NOCs to join and show measurable results by the next COP.”
Bjørn Otto Sverdrup, head of the OGDC Secretariat, said, “With OGDC, we have established a platform for companies willing to take action and collaborate across North, South, East, West, to share best practices and accelerate decarbonisation – particularly towards reducing methane and zero flaring by 2030.”
“We are encouraged by the progress made, and we look forward to the work ahead.”
At COP30, TotalEnergies announced a US$100mn commitment to Climate Investments Venture Strategy funds, which supports technologies that cut emissions across the oil and gas value chain. Climate Investments (CI) is an OGDC Partner.