In The Spotlight
AD Ports Group has reported continuation of all operations across its clusters without any disruption given current regional developments
The Group has already taken precautionay measure with the activation of its crisis management and business continuity protocols, as it remains in constant coordination with the authorities concerned in the UAE to safeguard its workforce, partners and stakeholders.
All UAE ports and terminals managed and operated by the Group’s Ports Cluster, in addition to related services remain fully operational.
While inaccessibility of the Strait of Hormuz will affect vessel calls at Khalifa Port, services at the port will go on uninterrupted. Closure of the Strait of Homruz will be compensated by increased volumes from the Group's diversified global maritime network, as it shifts trading routes.
Across the Group’s Maritime & Shipping Cluster, the majority of its 122 shipping vessels including container, bulk, Ro-Ro, and multipurpose vessels are operating outside the Strait of Hormuz. Those currently within the Strait continue to operate intra-Gulf services. Overall, the impact on the Maritime & Shipping Cluster is expected to be limited. The Group’s Economic Cities & Free Zones and Logistics Clusters are likewise expected to experience limited impact.
Captain Mohamed Juma Al Shamisi, Managing Director and Group CEO of AD Ports Group, said: “Global trade has historically demonstrated resilience during periods of geopolitical tension. Through disciplined execution, operational excellence and proactive risk management, AD Ports Group remains well positioned to support supply chain stability and uphold its commitments to customers across its global network, in line with vision with our wise leadership.’’
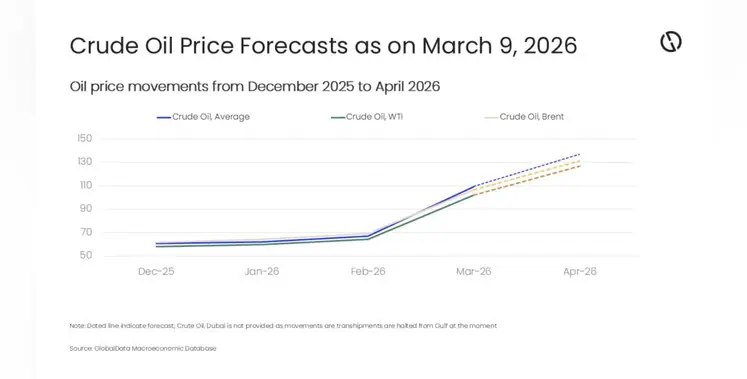
The oil market is no longer asking how much crude is being produced. It is asking who gets it, and when
Over the past week, attention has focused on the number of strikes across ports, refineries, power plants and LNG facilities in the Gulf. Depending on assumptions, the direct loss of wellhead, pipeline and refinery liquids to market may already exceed 1 million barrels per day. That figure alone is significant. But it remains secondary to the larger question hanging over the Strait of Hormuz.
Even if Hormuz begins to flow again in something close to normal volumes, the region’s infrastructure is clearly vulnerable. The market is now being forced to price not just a temporary blockage, but the risk of ongoing disruption to oil and gas facilities. Each passing hour of uncertainty adds incremental supply chain strain, and Brent has begun to reflect that reality.
There are various scenarios between full closure and full normalisation. Even a return to 75% of normal transit would present a severe logistical challenge. Insurance costs, naval escorts and rerouting all reduce effective supply. Freight markets are already reacting accordingly. Prompt tanker rates are surging, sharply raising landed crude procurement costs.
In this environment, traditional pricing logic begins to break down. The landed price of crude grades becomes less relevant when freight cannot be reliably fixed and spot premiums are difficult to establish. The market shifts from price optimisation to access management.
The West is relatively long crude and less dependent on Arabian Gulf supply than the East. It also holds freight advantages. Asia, by contrast, is more exposed to Gulf flows. As a result, refining runs in Asia are more at risk than in Europe or the United States. That divergence is already appearing in product markets via East-West spreads.
Brent-Dubai spreads may widen further regardless of freight direction. There is effectively no competition for the marginal Western barrel into Asia if Gulf supplies are constrained. In that context, Dubai-linked pricing can tighten independently of freight economics, while Brent can move in ways that do not necessarily align with historical arbitrage logic.
Freight costs themselves are becoming a direct transmission mechanism. Aframax rates to Europe imply roughly $9 per barrel to move WTI into the Atlantic Basin, pushing prompt WTI-Brent spreads wider. VLCC routes to Asia are similarly expensive. Yet benchmark differentials do not always adjust cleanly to reflect this because physical flows are constrained by risk, not simply by economics.
The longer the stand-off persists, the more structural these shifts become. Refiners must make procurement decisions based on security of supply rather than margin optimisation. Strategic reserves in the US, Europe, China, Japan and South Korea provide buffers measured in months, but releasing stocks is a policy decision. Governments may choose to loan or auction volumes to smooth disruption, but those tools are not immediate substitutes for steady Gulf exports.
Infrastructure risk now extends beyond crude production. There are concerns around storage capacity, with reports suggesting some export terminals may face tank-top pressures if flows remain restricted. Ullage becomes part of the conversation. Even if Hormuz reopens, infrastructure security will remain in question for some time.
Products will increasingly act as the demand-adjustment valve. Refining margins may need to rise to justify higher crude procurement costs and ensure available barrels flow eastward. Natural gas pricing is already signalling potential substitution toward fuel oil and crude in power generation where possible.
For now, the market’s priority is evidence that Hormuz can move safely and consistently, including clarity on insurance and escort arrangements. Without that, prices will continue to reflect supply chain risk rather than just supply loss.
This is no longer simply a production story. It is a logistics and allocation story. In a fragmented and risk-sensitive market, oil does not disappear evenly. It becomes a question of access, geography and timing. And that is where volatility truly begins.
The writer of the article is Neil Crosby, AVP Oil Analytics at Sparta
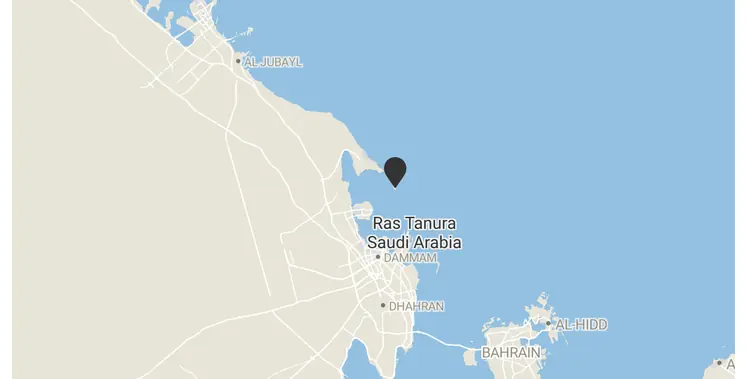
An official source at Saudi Arabia’s Ministry of Energy has confirmed that the Ras Tanura oil refinery sustained limited damage on Monday morning after debris from intercepted drones fell in its vicinity.
According to the Saudi Press Agency, the incident occurred at approximately 7:04 AM local time when two drones were intercepted near the facility. Falling fragments reportedly caused a small fire within the refinery complex.
Emergency response teams acted swiftly to contain the blaze, preventing any escalation. Authorities said the fire was brought under control in a short period of time, and no injuries or fatalities were recorded as a result of the incident.
As a precaution, certain operational units at the refinery were temporarily shut down while safety checks were carried out. Officials stressed that the measures were taken to ensure the continued protection of personnel and infrastructure.
Despite the disruption, the Ministry of Energy confirmed that the incident has not affected the supply of petroleum products to domestic markets. Fuel deliveries and distribution channels are continuing as normal, with contingency protocols ensuring stability in local supply chains.
Ras Tanura is one of the Kingdom’s key refining hubs, playing a central role in processing and distributing petroleum products. While the reported damage was described as limited, the event underscores the importance of protective and rapid-response measures at critical energy infrastructure sites.
Authorities have not released further details regarding the origin of the drones or the broader security context surrounding the interception. However, officials reiterated that safeguarding energy facilities remains a top priority, with emergency and security teams maintaining heightened vigilance.
The situation remains under monitoring, with the Ministry indicating that updates will be provided if necessary.

The strategic partnership agreement sets out the framework for NOC and MOL to exchange information and jointly explore potential areas of cooperation. (Image source: Adobe Stock)
Hungary’s MOL Group has signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with Libya’s National Oil Corporation (NOC) for cooperation in hydrocarbons exploration, technological innovation and crude trading, as international interest in Libya hots up
The strategic partnership agreement sets out the framework for NOC and MOL to exchange information and jointly explore potential areas of cooperation. These include hydrocarbon exploration and production, technological and field development innovations, oilfield services opportunities in Libya, crude supply and trading activities.
"We recognise Libya’s oil and gas industry as a pillar of strength and expertise. I am sure that this new agreement will act as a catalyst for further expanding our international portfolio, creating clear mutual value for both companies and reinforcing the resilience of our region. From the perspective of security of supply and energy sovereignty, particularly for landlocked countries, diversification of sources is of crucial importance. Our cooperation also goes beyond business, as we have agreed to rebuild our educational, scientific, and university ties in order to learn as much as possible from each other. Such partnerships can also help Europe to find its own path to competitiveness, rather than switching between different forms of energy dependency,” – said Zsolt Hernádi, chairman and CEO of the MOL Group.
The agreement comes as MOL is looking to expand its international portfolio to maintain its strategy target of at least 90,000 barrels of oil equivalent/day production level over the next five years, recently signing cooperation agreements with the national oil company of Kazakhstan (KazMunayGas), the national oil company of Azerbaijan (SOCAR), and the national oil company of Türkiye (Turkish Petroleum). The company has oil and gas exploration and production assets in nine countries, with production in eight countries: in Croatia, Azerbaijan, Iraq, Kazakhstan, Russia, Pakistan, Egypt, and Hungary.
The agreement also reflects the hotting up of international interest in Libya. Chevron recently signed an MoU with NOC to evaluate exploration and development opportunities, while TotalEnergies has signed an agreement extending the Libya Waha Concessions up to 2050, paving the way for further investments. TGS has a global provider of energy data and intelligence, has just signed a Letter of Intent (LOI) with North Africa Geophysical Company, (NAGECO),a subsidiary of the NOC to advance high-quality subsurface data, supporting Libya’s upstream development through modern, fit-for-purpose data and technology solutions. Libya’s latest upstream licensing round launched in March 2025, the first in 18 years, has attracted more than 40 bids, signalling growing international interest in Libya’s largely untapped hydrocarbon potential.
A wave of force majeure declarations has swept through the Middle East's energy sector this month as the ongoing US-Israel war with Iran disrupts production, shipping, and exports across the Gulf region, writes Sania Aziz.
The declarations, which relieve companies from contractual obligations due to unforeseen events beyond their control, stem from Iranian retaliatory attacks on facilities, threats to maritime routes, and the near-total blockage of the Strait of Hormuz, which is a vital chokepoint for one-fifth of global oil supplies.
QatarEnergy, the world's largest liquefied natural gas (LNG) exporter, was among the first to act. On 4 March, the state-owned firm declared force majeure on LNG shipments after halting production at key facilities in Ras Laffan and Mesaieed following Iranian drone strikes.
The company cited attacks on its infrastructure and the inability to operate safely, with sources indicating restarts could take weeks or longer to avoid equipment damage.
Qatar supplies around 20% of global LNG, and the move has sent shockwaves through Asian and European markets reliant on these deliveries.
Kuwait Petroleum Corporation (KPC) followed suit on 7 March, declaring force majeure on crude oil and product exports while slashing output.
The decision was prompted by explicit Iranian threats to shipping safety in the Strait of Hormuz, ongoing regional attacks, and a severe shortage of available vessels in the Gulf.
KPC, a major naphtha and jet fuel supplier to Asia and Europe, cited these factors as making normal operations impossible.
Bahrain's Bapco Energies joined the list today, 9 March, announcing force majeure on group operations after an Iranian strike set its Sitra refinery ablaze, which is the kingdom's sole refining complex.
The company assured that domestic supplies remain secure under contingency plans, but exports and broader activities are severely impacted by the conflict.
Aluminium Bahrain (Alba), operator of one of the region's largest smelters, declared force majeure earlier in March on shipments.
Unlike others, Alba stressed that its facilities remain undamaged; the issue lies solely in halted shipping through the Strait of Hormuz, preventing outbound metal deliveries despite continued production.
The ripple effects extend beyond Gulf producers. China's Wanhua Chemical declared force majeure on for supplies to Middle East customers, blaming severe regional shipping disruptions.
These developments have driven oil prices sharply higher and raised fears of prolonged supply shortages.
Analysts warn that further escalations could prompt additional declarations from Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and others as storage fills and export routes remain blocked.
The situation remains fluid, with global energy markets on high alert.
Aramco, Honeywell and King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) are collaborating to scale up the development of Crude-to-Chemicals (CTC) technology in a bid to maximise the value of crude oil and reduce costs associated with CTC conversion
The new CTC pathway will entail converting crude oil directly into light olefins and other high-demand chemicals, resulting in improved fuel efficiency, carbon utilisation, and process economics—allowing for more efficient and cost-effective production at scale.
The collaboration aligns with Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 by helping to advance economic diversification, build national research and technology capabilities, and strengthen the Kingdom’s position in the global chemicals market, combining academia and industry expertise to accelerate technology development and national capabilities.
Dr. Ali A. Al-Meshari, Aramco senior vice president of technology oversight & coordination, said, “This collaboration with Honeywell UOP and KAUST furthers Aramco's efforts to drive innovation and shape the future of petrochemicals. By harnessing the power of cutting-edge technologies, we aim to enhance energy efficiency and unlock increased value from every barrel of crude. This novel Crude-to-Chemicals process is aligned with our vision of supporting the global transition towards cleaner, high-performance chemical production. Moreover, this initiative demonstrates our focus on contributing to the growth of a vibrant ecosystem, where the deployment of innovative technologies can create lasting value for our stakeholders, our communities, and the environment.”
Rajesh Gattupalli, Honeywell UOP president, added, “This agreement marks a defining moment in our strategic collaboration with Aramco and KAUST – and in the global evolution of Crude-to-Chemicals technology. With Honeywell UOP’s deep expertise in catalytic process design and commercial scale-up, we’re well positioned to drive this innovation forward.”
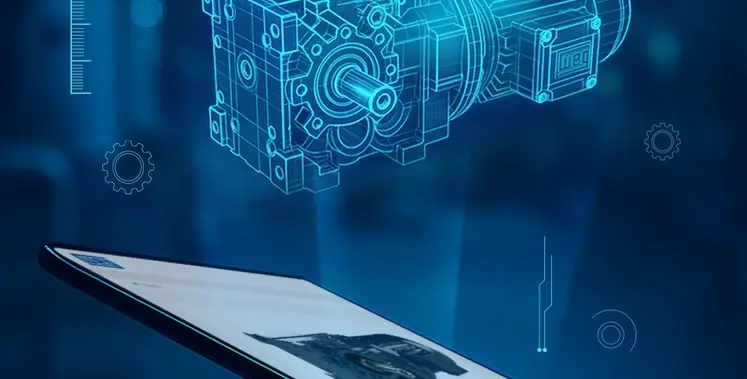
Manufacturing company, WEG, has introduced a digital tool called Gear ProSelect, that will simplify and standardise the selection, configuration and documentation of gearboxes and gearmotors
Developed as a single global solution, the tool ensures consistency for sizing across regions while reducing the time typically required for manual calculations or engineering support.
As the gearbox market expands alongside industrial automation, it can shoot up to US$33.4bn this year. To match the market dynamism, clients require standardised and digitally-driven selection methods.
With this thought, WEG has developed Gear ProSelect (GPS) which lets users size and configure gearboxes directly through a web-based platform using application-specific data. By entering parameters such as mass, speed and inertia, users receive product recommendations supported by integrated mechanical and thermal validation.
The thermal validation feature represents a unique differentiator in the market. Thermal validation analyses heat generation and dissipation under defined operating conditions, ensuring the selected gearbox can operate within acceptable temperature limits and reducing the risk of overheating or premature wear.
“Gear ProSelect represents a major step forward in WEG’s digital transformation strategy,” said Marcio Yoshikazu Ematsu, European marketing manager at WEG. “By combining intelligent validation, real-time visualisation and global standardisation, we are providing customers with greater autonomy while strengthening operational efficiency across our worldwide network.”

Oil and gas operations in the Middle East span harsh deserts, sprawling refineries and high-risk offshore environments. (Image source: Adobe Stock)
In the oil and gas industry, where every second counts and every decision impacts profitability and safety, robust security is not just a luxury – it's a necessity
From protecting critical assets to safeguarding human lives, security systems must meet the highest standards of reliability and performance.
Pelco, a leader in video security, is uniquely positioned to address the challenges faced by oil and gas companies in the Middle East, offering a fresh perspective on how to optimise security systems seamlessly. With our upcoming online event, we invite you to explore how Pelco can help tackle worker safety, asset protection and operational efficiency in this complex industry.
Addressing oil and gas challenges head-on
Oil and gas operations in the Middle East span harsh deserts, sprawling refineries and high-risk offshore environments. Physical, environmental and digital threats are converging, and security systems must evolve to meet these overlapping demands. Our upcoming online event will focus on three critical areas where Pelco's expertise can make a difference:
1. Improve worker safety and HSE compliance
Ensuring worker safety is both a moral responsibility and a regulatory imperative. Health, Safety and Environmental (HSE) compliance is a top priority for oil and gas operations. Pelco's advanced portfolio is designed to help you meet these standards.
Edge-based analytics and intelligent video security can be valuable tools in supporting site safety. These systems can help detect safety incidents, such as slips or falls, especially in areas where oily surfaces, heat or dust create additional hazards. When incidents occur in remote areas, automated detection can prompt faster intervention, thereby closing the gap between the event and the response.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) compliance is another key safety concern. High temperatures in the Middle East can lead to discomfort, and in some cases, workers may be tempted to remove protective gear, such as hard hats or vests, for temporary relief. In this case, AI-enabled video analytics can help identify instances of non-compliance, enabling safety teams to address the issue before it becomes a liability.
Zone-based behavioural analytics can help detect when someone enters a restricted or hazardous area or remains in a dangerous zone longer than necessary. For example, loitering detection near flare stacks or storage tanks can support situational awareness and proactive incident mitigation.
2. Improve security and asset protection
From refineries in the desert to offshore rigs in corrosive marine environments, your assets operate under pressure, so your security systems must withstand these harsh conditions. In areas where explosive gases or dust particles may be present, even basic equipment can pose risks. That’s why choosing video solutions built for hazardous environments is critical.
ExSite Enhanced cameras, featuring 316L stainless steel construction and certifications such as ATEX and IECEx, are designed for use in hazardous atmospheres. Whether it’s observing pipeline manifolds, wellheads or chemical storage areas, these systems deliver dependable performance in high-risk environments. In corrosive coastal locations, such as LNG terminals or offshore rigs, Pelco’s anti-corrosion models withstand salt spray, humidity and chemical exposure without compromising visibility.
For perimeter defence, long-range Silent Sentinel cameras give security teams early warning of approaching threats, detecting vehicles, vessels or drones from kilometres away in fog, darkness or dust. These systems are especially valuable for remote desert pipelines or unstaffed offshore installations, where rapid detection is critical to prevent disruptions.
3. Minimise downtime and maximise uptime
Every minute of downtime impacts revenue. For oil and gas operations, the cost of unplanned outages is measured in millions of dollars. With Pelco, your video security can become an operational asset.
Radiometric thermal cameras can detect overheating in transformers, compressors and electrical panels, allowing teams to take action before equipment failure occurs. At the same time, Pelco’s camera image health analytics help ensure your video infrastructure is always performing at its best. Our cameras automatically detect issues such as lens obstructions, misalignment or tampering, reducing the need for manual inspections and helping ensure your security coverage is always clear, optimised and ready when it matters most.
Join us to discover the Pelco advantage
We invite you to join our upcoming online event, where industry leaders and Pelco experts will dive deeper into these challenges and solutions. Together, we'll explore how Pelco can be the missing ingredient to supercharge your security and drive operational excellence in the Middle East oil and gas sector.
Don't miss this opportunity to gain actionable insights and position your operations for success. Register now and discover how Pelco can transform your approach to security.

Progress has been reported in developing action plans to reduce methane emissions and end routine flaring. (Image source: Adobe Stock)
Coinciding with COP30, significant progress has been reported in driving forward the aims of the Oil & Gas Decarbonization Charter (OGDC) launched at COP28
The Oil & Gas Decarbonization Charter (OGDC), a global coalition of leading energy companies championed by the CEOs of ADNOC, Aramco, and TotalEnergies and supported by the Oil and Gas Climate Initiative (OGCI), highlights expanded reporting coverage, strengthened action plans for emissions reduction and enhanced collaboration to accelerate industry decarbonisation in its 2025 Status Report: Implementing Action.
The Charter now brings together 55 signatories operating across more than 100 countries, representing around 40% of global oil production. Signatories invested approximately US$32bn in low-carbon solutions including renewables, carbon capture, hydrogen and low-carbon fuels in 2024.
This year, for the first time, the companies shared emissions data based on the OGCI Reporting Framework, laying the foundation for consistent reporting across 55 companies. 50 of the 55 signatories submitted data for this year’s report, covering 98% of OGDC operated production, most of which has received third-party assurance.
Forty-two signatories have now set interim Scope 1 and 2 emissions reductions ambitions for 2030, and 36 have developed corresponding action plans, reflecting tangible progress since the Charter’s 2024 Baseline Report, with six more companies sharing interim ambitions and seven more developing corresponding action plans on methane and flaring.
Extensive collaboration programme
An extensive collaboration programme is underway, with a focus on methane, flaring and reporting. TotalEnergies for example is sharing its AUSEA technology with several national oil companies to strengthen methane detection and measurement. Peer-to-peer exchanges, regional partnerships and technical workshops have strengthened capacities, while engagement with OGCI, the United Nations Environment Programme, the World Bank and many others, are helping scale practical solutions. At the company level, OGDC is helping to embed tailored, industry-specific training programmes.
Dr Sultan Ahmed Al Jaber, managing director, Group CEO of ADNOC, COP28 president and OGDC CEO Champion, said, “Two years ago, at COP28 we came together to create the world’s first truly industry-wide coalition to decarbonise at scale. Together, we are turning the Charter’s words into action by delivering tangible progress, scaling innovation and reporting transparently against our shared commitments.”
Patrick Pouyanné, chairman and CEO of TotalEnergies and OGDC CEO Champion, added, “OGDC is about action and collective delivery. This year we moved from baseline to implementation, with almost all signatories reporting data that covers 98% of operated production and more companies setting 2030 targets backed by plans. This reflects that progress starts with what we measure and a shared reality that this is a journey where we advance faster together. Our focus now is clear. We must cut methane, end routine flaring and report progress consistently. We invite all IOCs and NOCs to join and show measurable results by the next COP.”
Bjørn Otto Sverdrup, head of the OGDC Secretariat, said, “With OGDC, we have established a platform for companies willing to take action and collaborate across North, South, East, West, to share best practices and accelerate decarbonisation – particularly towards reducing methane and zero flaring by 2030.”
“We are encouraged by the progress made, and we look forward to the work ahead.”
At COP30, TotalEnergies announced a US$100mn commitment to Climate Investments Venture Strategy funds, which supports technologies that cut emissions across the oil and gas value chain. Climate Investments (CI) is an OGDC Partner.